Need assistance?
Need Assistance? Call Us 0330 058 0631





















 Book a service
Book a service











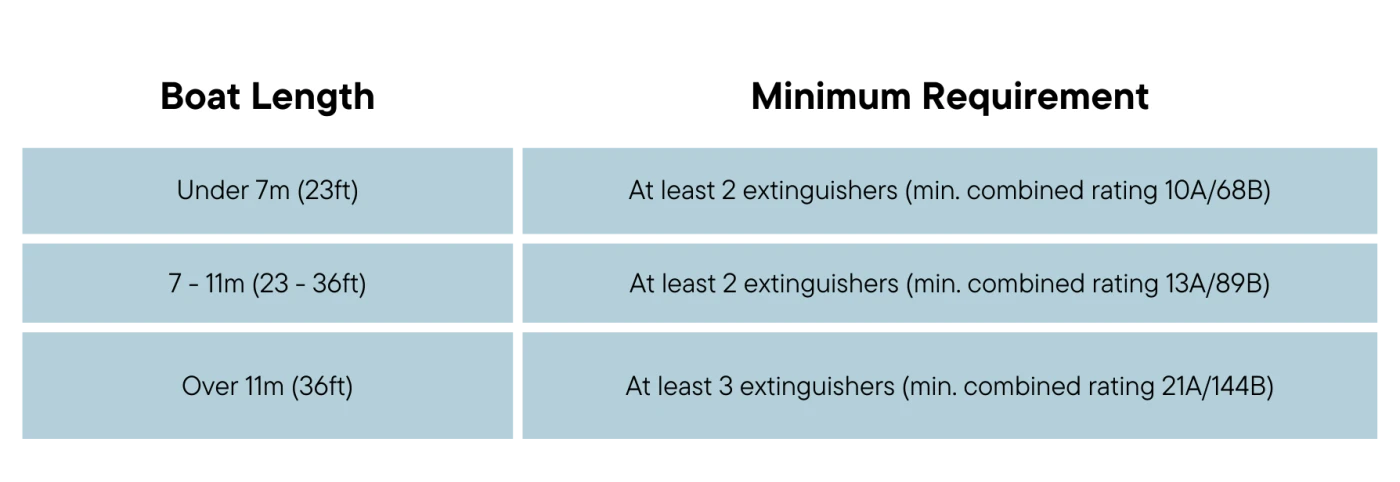
To meet Boat Safety Scheme (BSS) requirements for passenger boats, any boat fitted with an engine or with onboard equipment such as cooking, heating, refrigeration, or lighting must carry at least the minimum number of portable fire extinguishers shown in the table below.
Each portable fire extinguisher should have a fire rating of 5A/34B or higher.
A small, open passenger boat with no engine and no cooker only needs one fire extinguisher rated at 5A/34B.
Keep in mind: these minimum requirements are based on boat length, but they may not cover every fire risk. If your passenger boat has extra appliances, fuel systems, or other unique features, it’s worth considering additional extinguishers or ones with a higher fire rating.
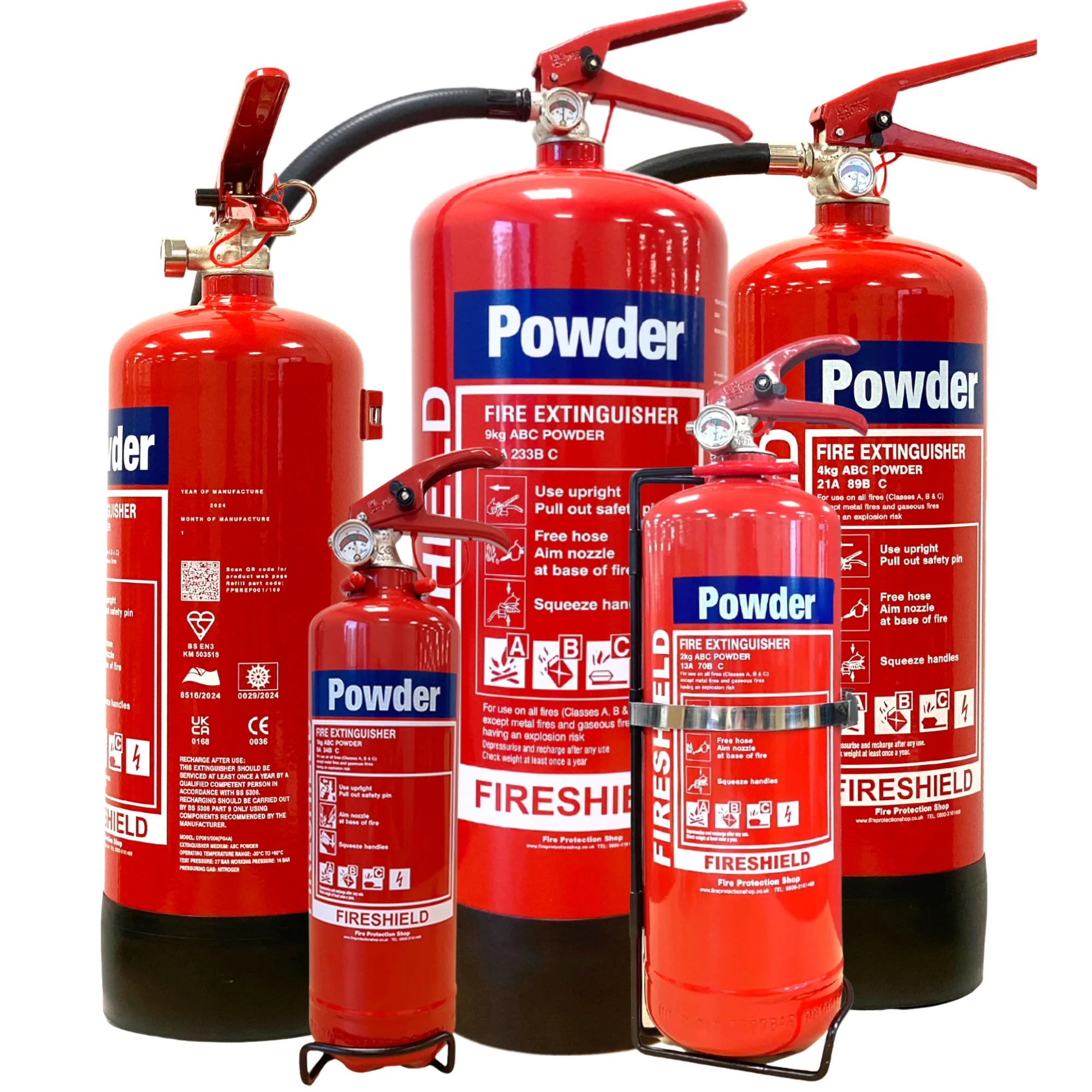
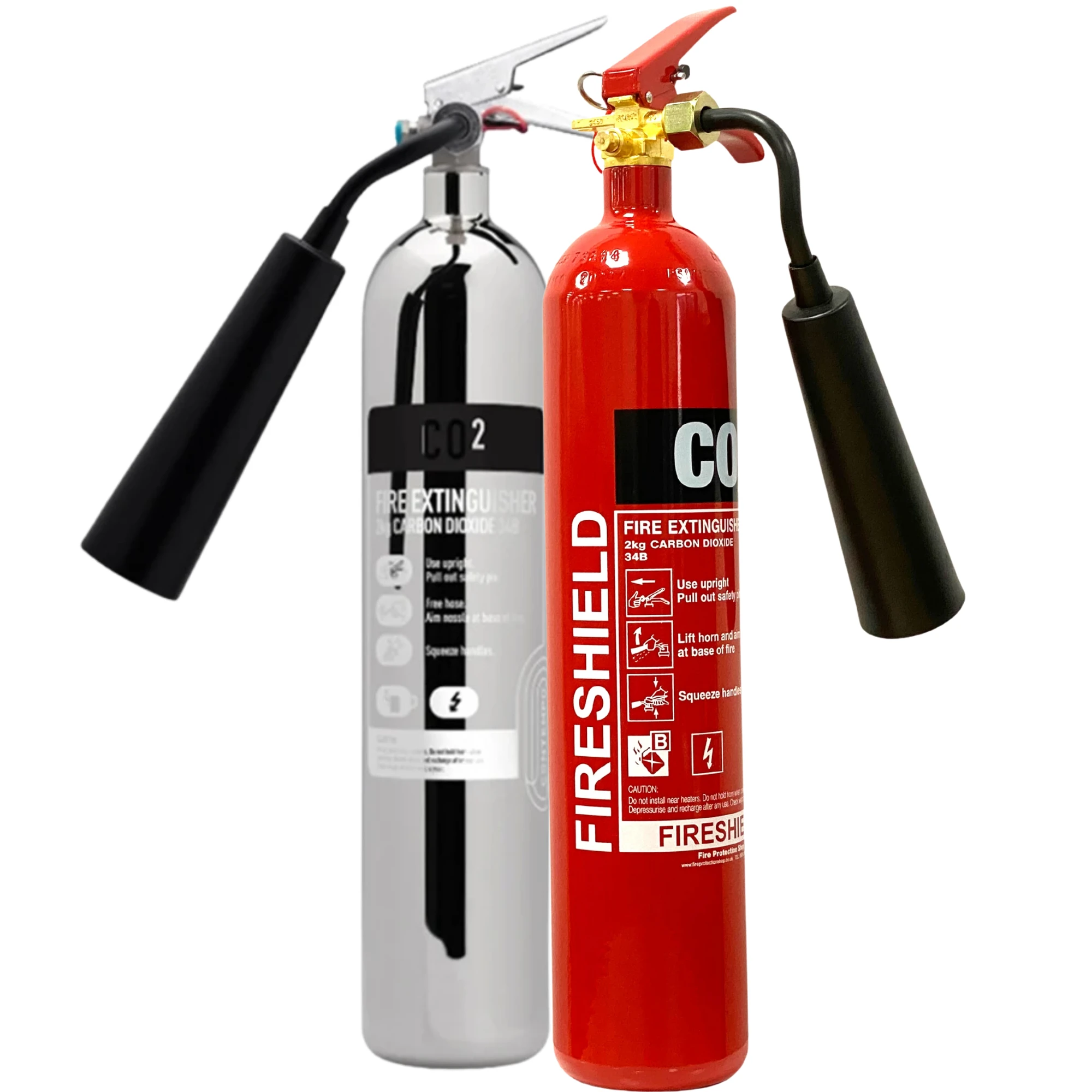
Many passenger boat operators choose dry powder extinguishers because they offer wide coverage across the most common onboard fire risks.
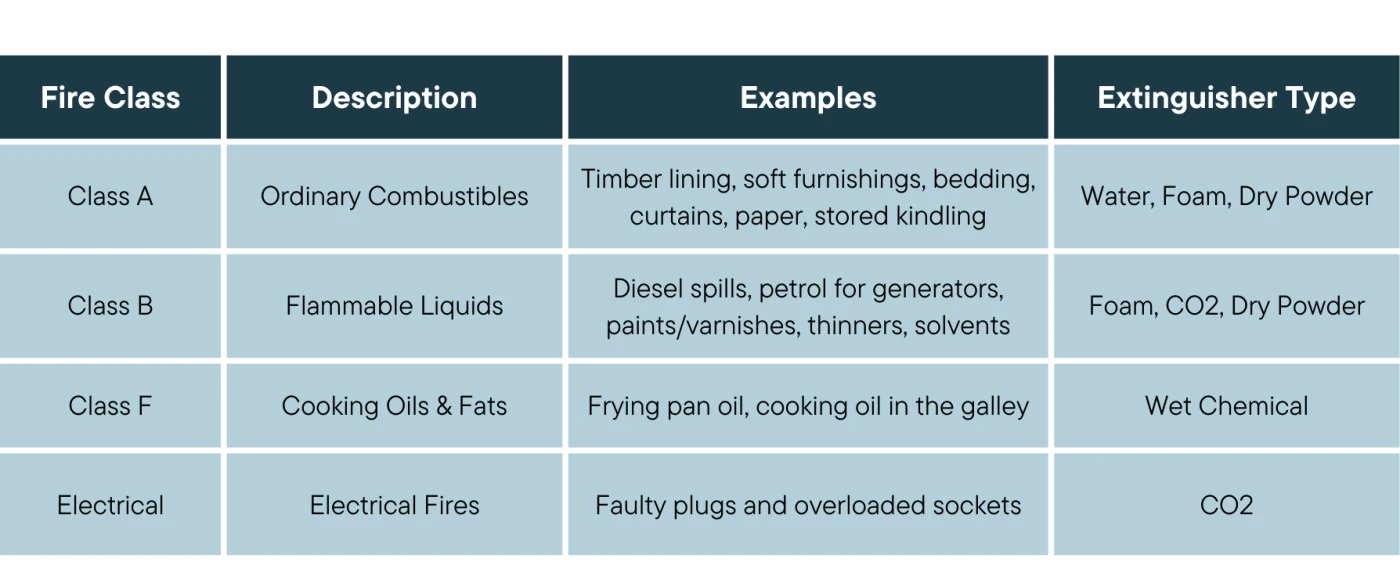
Dry powder extinguishers can be used for:
Class A fires (combustible solids)
Class B fires (flammable liquids)
Class C fires (flammable gases)
Live electrical equipment fires
Dry powder extinguishers are compact, easy to mount, and well-suited to passenger vessel hazards such as engine rooms, fuel systems, electrical faults, and galley or catering areas.
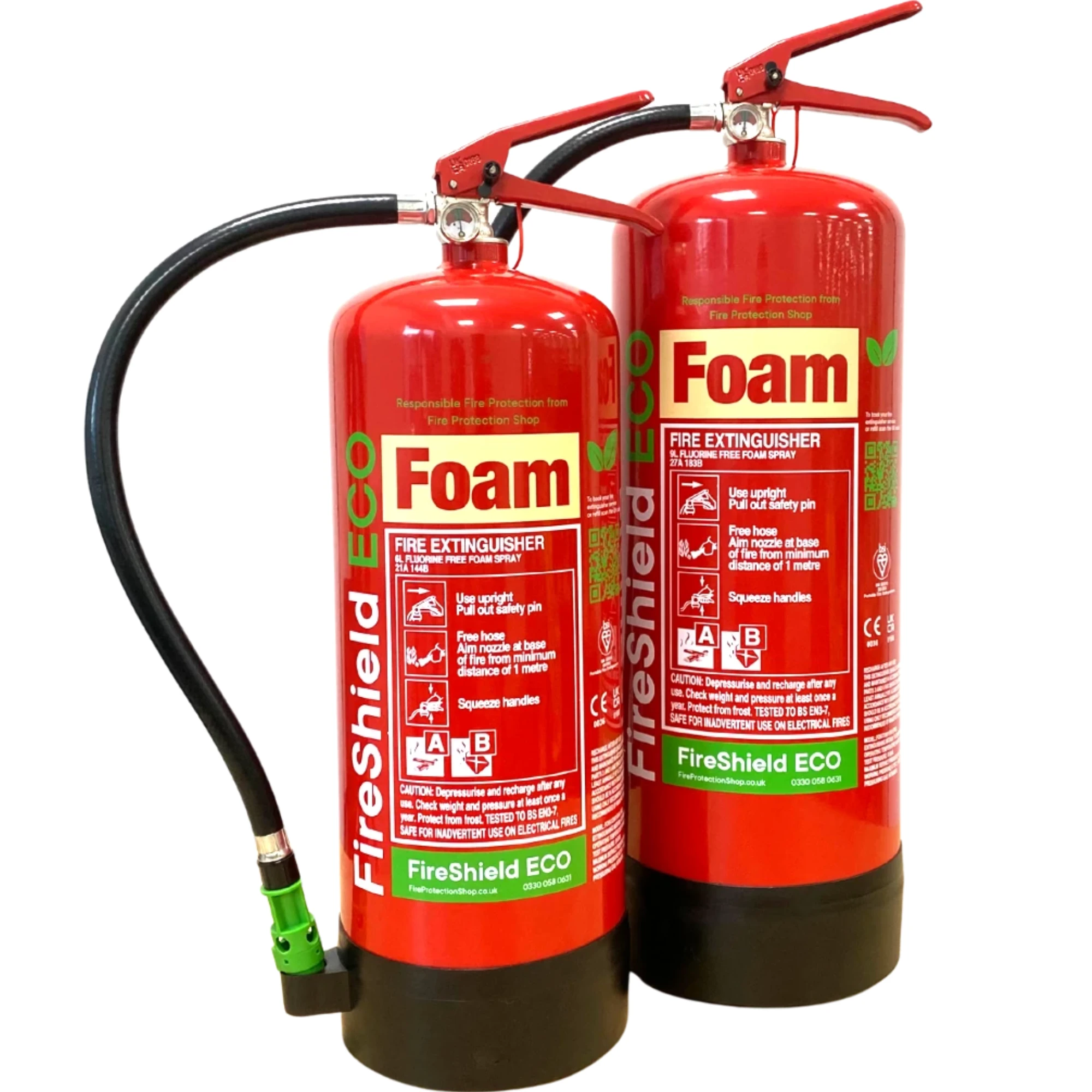
Because passenger boats are enclosed spaces and may carry multiple people, it’s important to note that dry powder can reduce visibility and create airborne dust that may cause breathing discomfort when discharged indoors. As a result, many operators use powder extinguishers for engine and technical areas, while opting for a fluorine-free foam extinguisher for cabins, passenger seating areas, and internal spaces. Foam offers protection for Class A and B fires and typically creates less airborne residue.
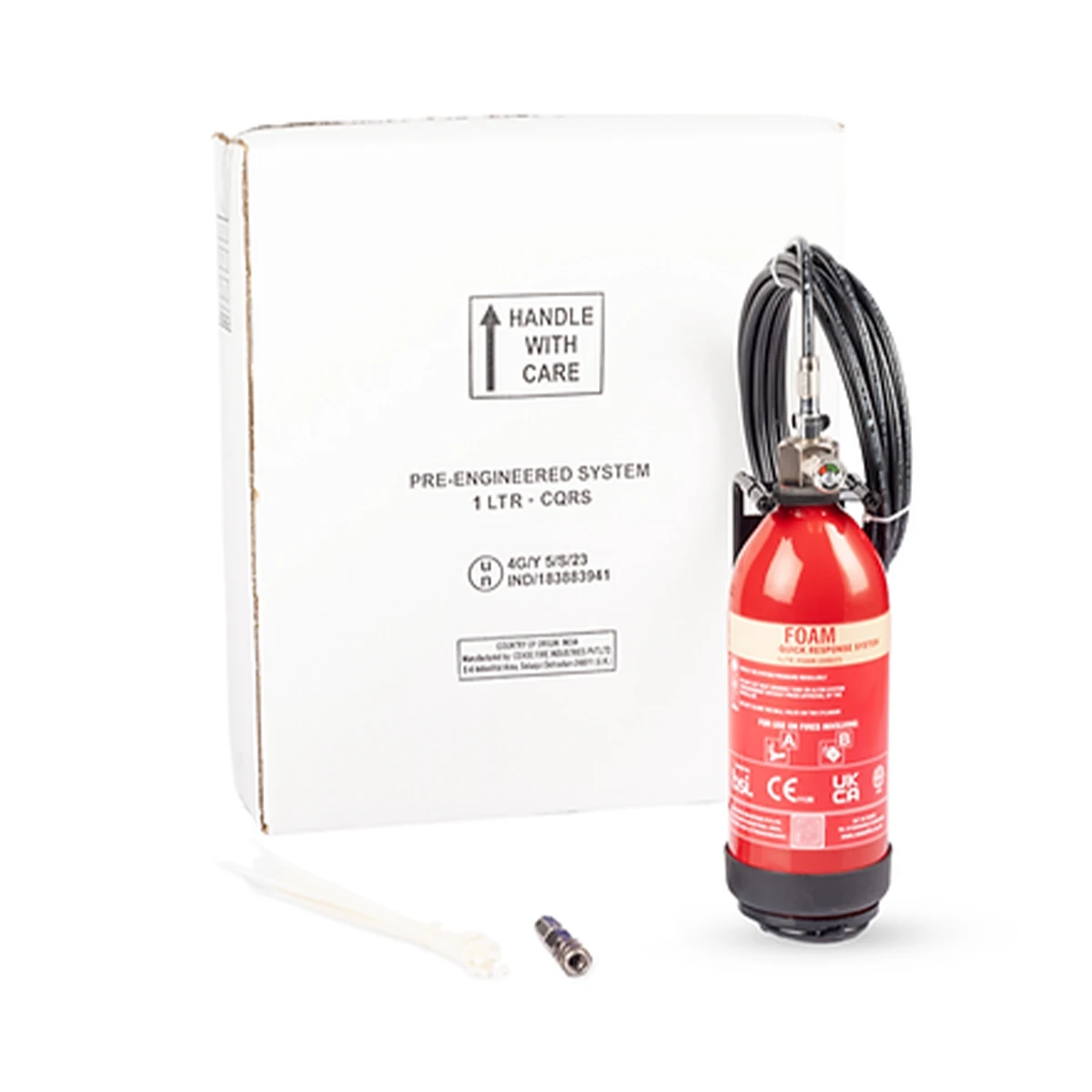
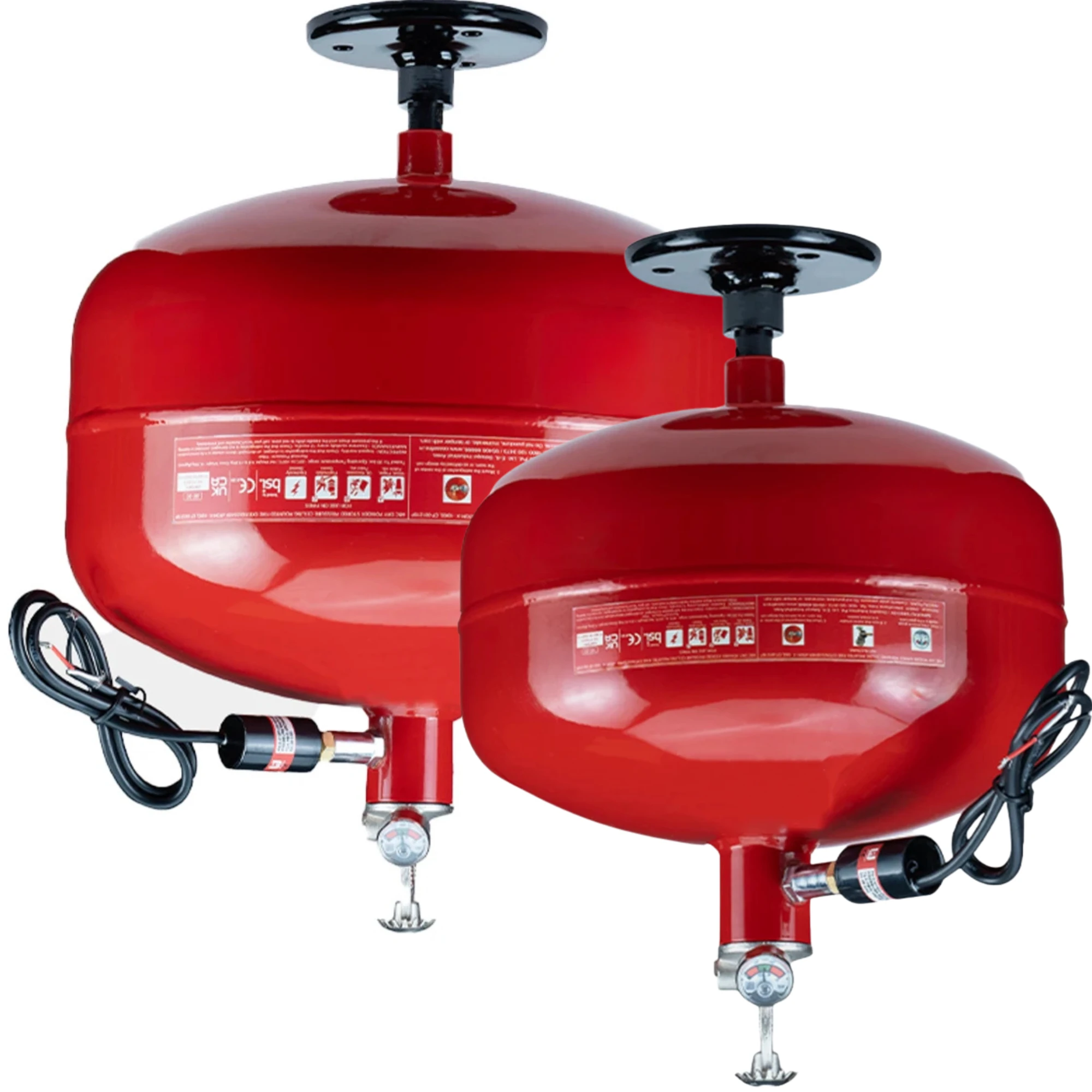
Due to these vessels carrying passengers, we recommend that boats install an automatic suppression system when covering engine fire risks. Automatic systems provide 24/7 unmanned protection, making them ideal for small compartments that are difficult to access. We supply tube-based automatic fire suppression systems, available in both dry powder and foam options.
Finally, a fire blanket is a common essential in the galley, providing a quick and effective way to deal with small cooking fires.
The requirements outlined in Part 6 of the 2002 Boat Safety Scheme Standards are compulsory for non-private vessels.
In the event of a fire on board, fire extinguishers must be quick and easy to access. They should be positioned in accessible locations close to the main fire risk areas, such as the engine compartment and the galley.
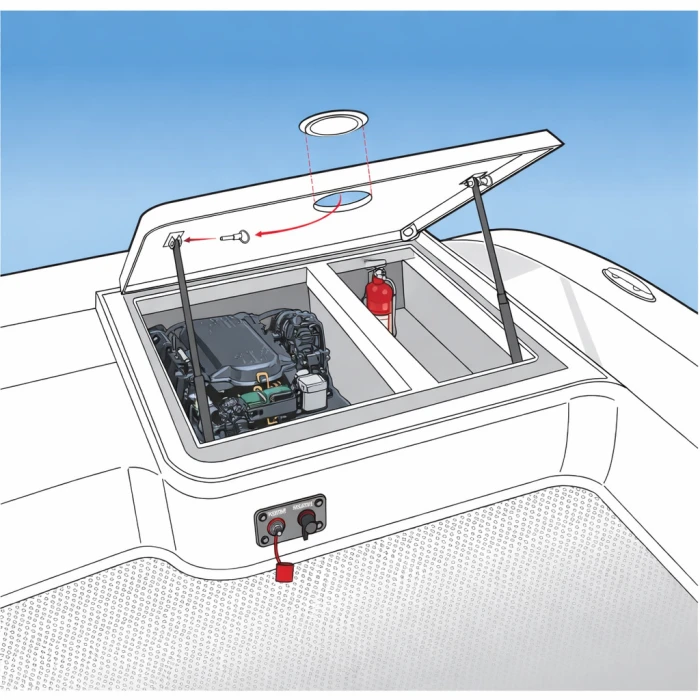
If a fire starts in an engine space, and extra air enters, this can cause the fire to intensify rapidly. To minimise this risk, any portable extinguisher intended for engine-space protection should be positioned in a space where you aren't required to fully open the main engine hatch or access panel. Important to note, we highly recommend an automatic system for engine spaces to avoid needing human input.
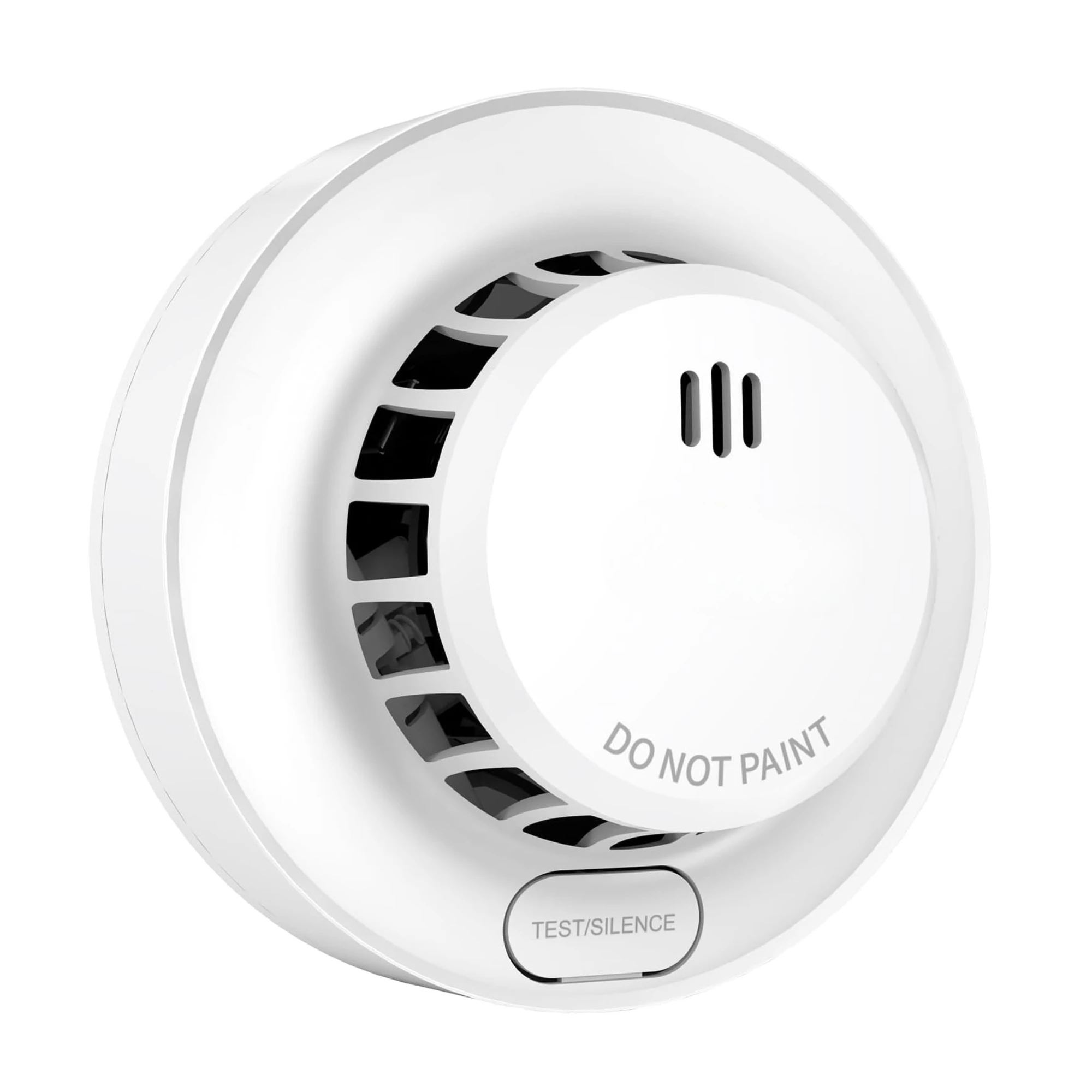
Many passenger boat operators fit smoke alarms and carbon monoxide (CO) alarms on their boats. Smoke alarms give an early warning of fire, helping you to respond quickly and support safe evacuation if necessary. CO alarms are especially important on passenger vessels where appliances, like heaters, generators, or engine exhaust systems, can produce carbon monoxide if ventilation is poor or flues are faulty.
Alongside alarms, it is best practice to keep a fully stocked first aid kit on board for minor injuries and emergency situations, especially when carrying passengers.
We also supply a range of fire extinguisher storage options, helping you to keep extinguishers safe, secure and visible in an emergency.
We use cookies to enhance your site experience. Choose your preferences below.